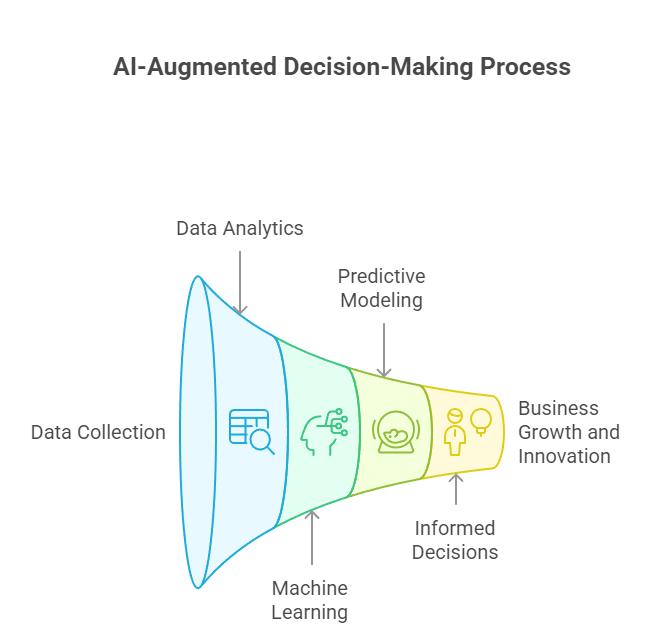
Introduction
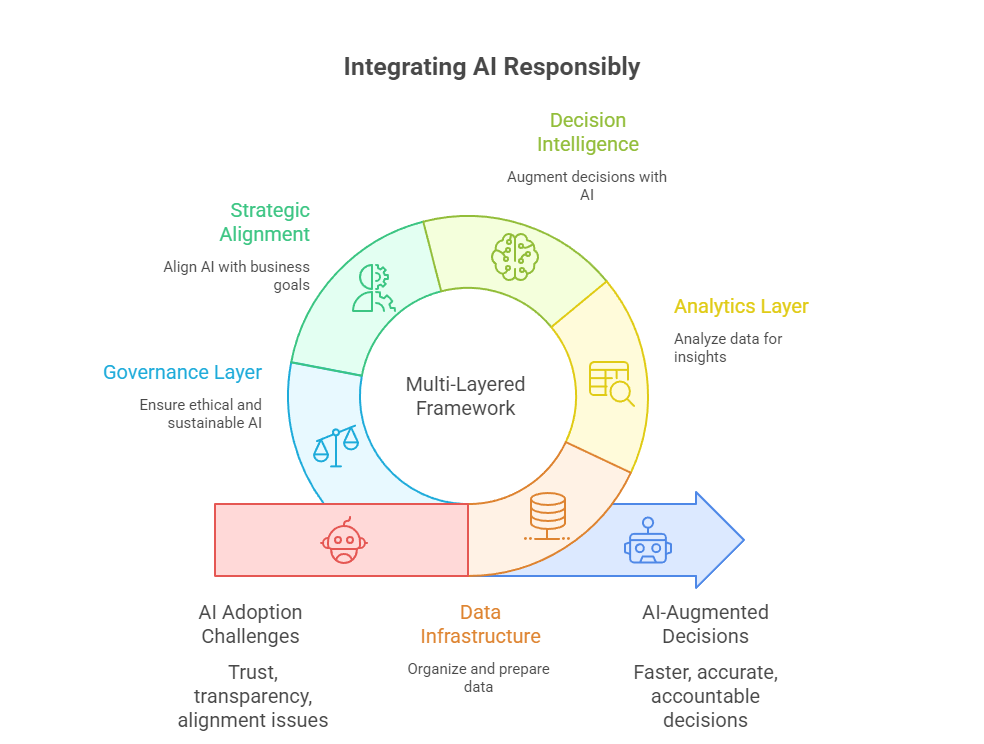
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping the way businesses operate, driving efficiency, accuracy, and innovation in decision-making processes. Yet, many organizations face challenges when it comes to trust, transparency, and alignment of AI outputs with strategic goals. To address these challenges, the Multi-Layered Framework provides a comprehensive roadmap for integrating AI responsibly and effectively into business ecosystems. By structuring AI adoption across layers—data infrastructure, analytics, decision intelligence, strategy, and governance—this framework helps organizations bridge the gap between technology and business value. In doing so, it empowers leaders to make AI-augmented decisions that are not only faster and more accurate but also accountable, ethical, and sustainable.
1. Data & Infrastructure
Data and infrastructure form the backbone of any AI-driven system. This layer ensures that data is collected, stored, and processed in ways that maintain quality, integrity, and compliance with privacy regulations. Key components include data pipelines, IoT sensors, cloud and edge computing, and strong data governance mechanisms. For businesses, this means establishing robust data management practices, including metadata tracking, lineage documentation, and security protocols. Without these foundations, AI systems risk producing biased or unreliable results. Moreover, standardized infrastructure allows seamless interoperability across departments and even with external partners, setting the stage for cross-organizational decision-making.
2. AI & Analytics
The AI & Analytics layer transforms raw data into actionable insights. Techniques such as machine learning, predictive modeling, reinforcement learning, and generative AI provide organizations with capabilities to forecast trends, optimize operations, and design innovative products. Central to this layer is Explainable AI (XAI), which ensures that models are interpretable and transparent to stakeholders. Additionally, tools like AutoML pipelines simplify model development, while monitoring systems detect concept drift, bias, or accuracy degradation over time. For organizations, this layer turns data into a competitive asset, offering not just answers but also justifications, thereby increasing stakeholder trust.
3. Decision Intelligence Core
At the core of the framework lies Decision Intelligence, where human judgment and AI capabilities converge. This layer focuses on creating effective human–AI teaming models, ensuring humans remain in the loop to provide contextual reasoning, ethical oversight, and adaptability in uncertain environments. Scenario modeling and simulation tools empower managers to test multiple outcomes before committing to a decision. Assurance mechanisms such as audit trails, bias detection, and robustness checks further strengthen decision legitimacy. By embedding transparency and accountability into the decision-making process, organizations can avoid the pitfalls of over-reliance on automation and ensure outcomes are both effective and ethical.
4. Strategic Alignment
The Strategic Alignment layer connects AI-augmented decisions to organizational objectives, risk appetite, and sustainability goals. This ensures that AI is not simply solving isolated problems but is actively driving the company’s mission and long-term growth. By aligning AI recommendations with key performance indicators (KPIs), businesses can measure their effectiveness and ensure compliance with ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) responsibilities. Dashboards and performance monitoring systems translate AI insights into meaningful business outcomes. This layer is critical for achieving buy-in from leadership and ensuring that AI initiatives remain relevant to stakeholders at all levels of the organization.
5. Ecosystem & Governance
The final layer extends AI-augmented decision-making beyond the enterprise to the broader ecosystem of partners, regulators, and customers. Ecosystem governance involves setting clear rules for data sharing, establishing interoperability standards, and building mechanisms for trust such as smart contracts, federated learning, and shared audit systems. This layer is vital as businesses increasingly operate in interconnected networks where value is co-created. By adopting strong governance practices, companies can mitigate risks related to data misuse, liability, and compliance, while also fostering innovation and collaboration across industries. Strong ecosystem governance transforms AI into a trusted capability that scales responsibly.
6. Continuous Learning & Adaptation
An often-overlooked dimension of AI adoption is the ability to continuously learn and adapt. AI models, like businesses themselves, must evolve with changing data, regulations, and market conditions. A continuous learning culture ensures that organizations do not stagnate but instead refine their AI-driven processes over time. This includes mechanisms for retraining models, updating governance policies, and reskilling employees to work effectively with evolving AI systems. In a rapidly changing digital economy, continuous adaptation ensures long-term resilience and competitive advantage.
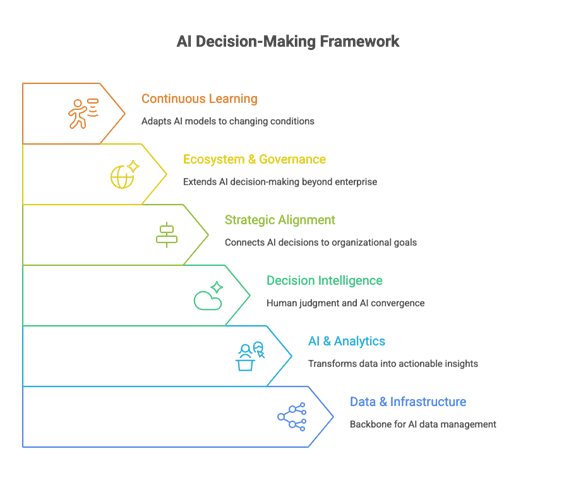
How the Multi-Layered Framework Helps Businesses
The Multi-Layered Framework empowers businesses to use AI not as a standalone tool but as a core driver of strategic and ethical decision-making. Data and infrastructure establish trustworthy foundations, while analytics and AI generate insights with transparency. The decision intelligence core ensures that humans remain central, reinforcing accountability. Strategic alignment ensures that AI outputs contribute to business growth and ESG goals, while governance extends trust across entire ecosystems. By incorporating continuous learning, the framework ensures adaptability to emerging risks and opportunities. Collectively, these layers allow businesses to take AI-augmented decisions that are resilient, responsible, and scalable.
Conclusion
The Multi-Layered Framework provides organizations with a structured and adaptable roadmap for AI adoption. It addresses both technical and managerial dimensions of decision-making, ensuring that AI initiatives are aligned with strategic goals, supported by governance, and scalable across ecosystems. By embedding transparency, human oversight, and adaptability at every layer, businesses can institutionalize AI-augmented decision-making that is trustworthy and sustainable. In today’s dynamic digital economy, organizations that adopt such a framework will be best positioned to leverage AI as a source of long-term value creation and competitive advantage.
References
1. Davenport, T. H., & Miller, A. (2022). Decision Intelligence: How AI Enhances Human Judgment in Business. Harvard Business Review. https://hbr.org/2022/10/decision-intelligence-how-ai-enhances-human-judgment-in-business
2. Shrestha, Y. R., Ben-Menahem, S. M., & von Krogh, G. (2021). Organizational Decision-Making Structures in the Age of Artificial Intelligence. California Management Review, 63(4), 46–69. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full/10.1177/00081256211032687
3. OECD. (2024). OECD Framework for the Classification of AI Systems: Responsible AI Principles. OECD AI Policy Observatory. https://oecd.ai/en/classification
4. Ghosh, R., & Aggarwal, R. (2023). MLOps and Explainable AI for Scalable Decision Intelligence. MIT Sloan Management Review. https://sloanreview.mit.edu/article/mlops-and-explainable-ai-for-scalable-decision-intelligence/
5. Brynjolfsson, E., & McAfee, A. (2017). Machine, Platform, Crowd: Harnessing Our Digital Future. W. W. Norton & Company.
Author:
Nafiz Imtiaz
Operations Analyst Intern
Inuberry Global
GET IN TOUCH
